Knowledge Centre
Maximizing Rubber Performance: The Essential Role of High Forces DMA GABO EPLEXOR 500 N in Tire Testing
For the automobile tyre business to ensure efficiency and safety on the road, rubber compound performance and durability must be optimized. A valuable instrument for material testing, the High Forces DMA GABO EPLEXOR 500 N provides accurate information on the characteristics of materials under many circumstances. It is an essential part of the tire development…
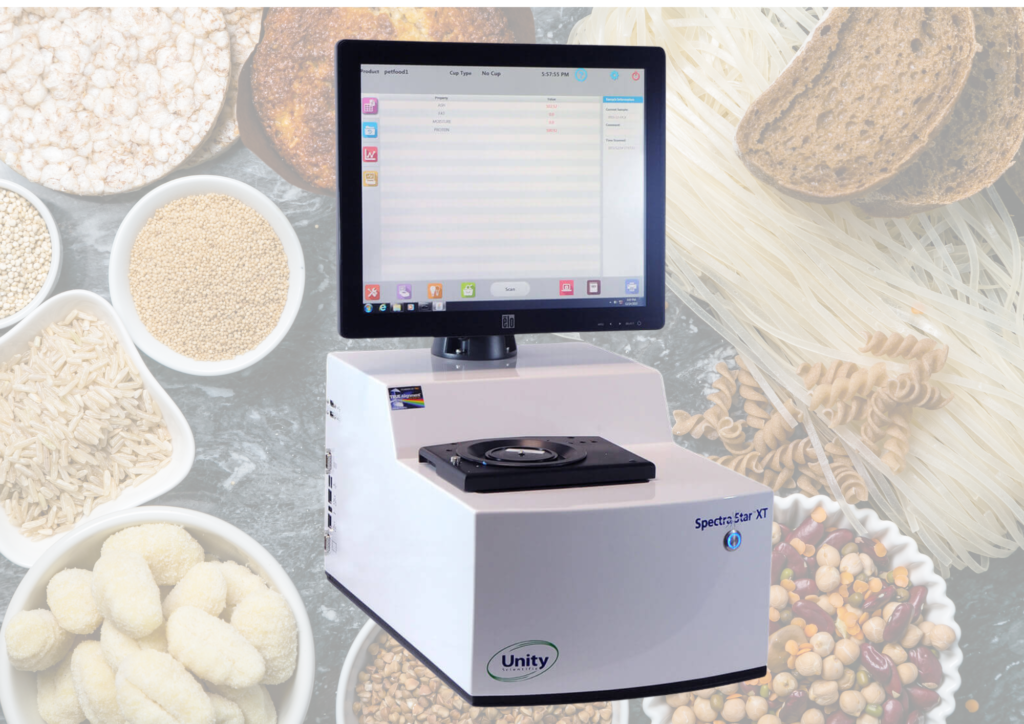
Read MoreNear-Infrared Food Analyzer: Unity® SpectraStar™ XT series
The Unity® Scientific SpectraStar™ XT NIR Analyzer Series is a comprehensive line of solutions for laboratory and at-line compositional analysis for an extensive range of food samples such as wheat, flour, snacks, chocolate, feed, forage products etc. The compact bench top model with user-friendly UScan software interface, it allows you to effortlessly conduct a comprehensive…
Read More
Laser Diffraction Academy:
How to choose the right Dispersion Accessories for your samples
Particle Characterization In the technique of Particle Size Analysis, the distribution of sizes in a sample, either of solid or liquid particulate material is measured and reported. This analytical technique is important to characterize a wide range of final-product performance factors. Combining a modern sizing technique and state of the art nanoparticle measurement, the LA-960V2…
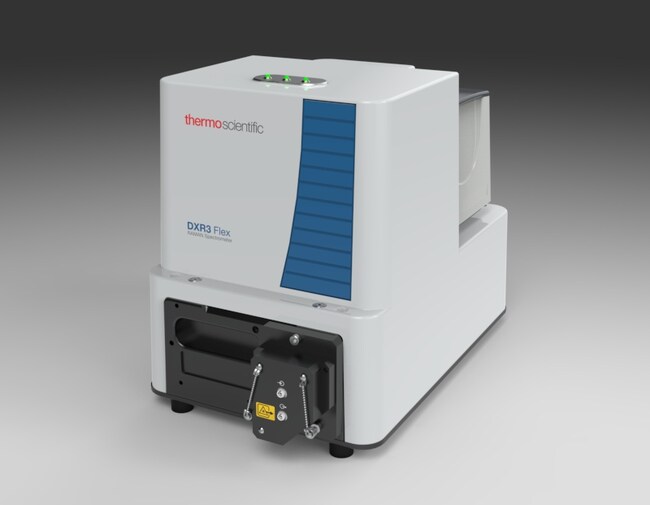
Read MoreBroaden your Raman analysis options
Expand the range of sampling capabilities with the new Thermo Scientific DXR3 Flex Raman Spectrometer. The DXR3 Flex offers you numerous sampling modes that allow for rapid, high-quality data capture on any number of samples. Options include a bulk material “macro” sampler, a single point microscope accessory with manual stage, and fiber optic probes. Read…
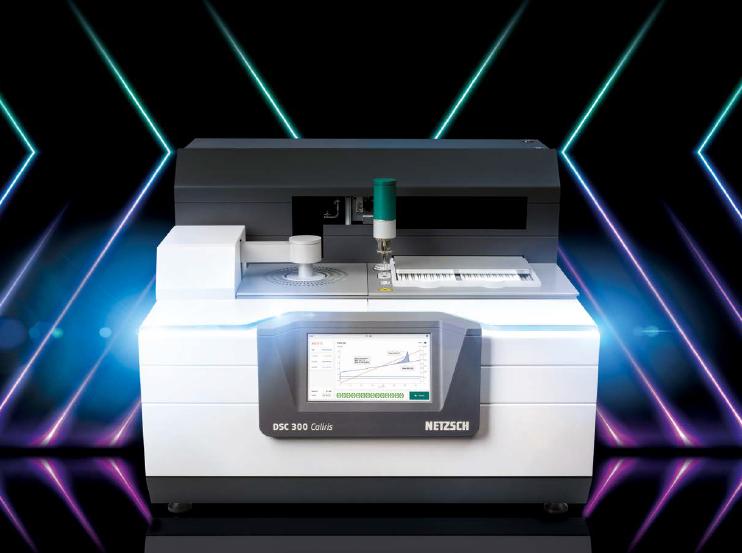
Read MoreThe Differences of DSC 300 Caliris® Supreme and Select
DSC 300 Caliris® Supreme & Select The newly launch DSC 300 Caliris® is designed to meet customers’ demands of modularity, flexibility & simple operating procedures. The Caliris® is available in 2 versions the Supreme or Select. DSC 300 Caliris® Supreme – comes with 3 modules that is interchangeable by customers. This upgrade makes it possible…
Read MoreDETERMINATION OF MERCURY (Hg), ARSENIC (As), SELENIUM (Se), ANTIMONY (Sb) AND BISMUTH IN CLINICAL SAMPLES USING ATOMIC FLUORESCENCE SPECTROMETRY
The determination of toxic metals Hg, As and Sb in biological samples of humans is an important clinical screening procedure. Exposure of these metals from the diet, local surroundings and industrial & occupational processes can lead to serious and significant health issues.
Analyzing the total concentration of these elements is important but, by no means, the whole story.
USING ATOMIC FLUORESCENCE SPECTROMETRY FOR THE DETERMINATION OF MERCURY (Hg), ARSENIC (As), SELENIUM (Se), ANTIMONY (Sb) IN ENVIRONMENTAL SAMPLES
Soils are the major sink of these metal contaminants, while in aquatic systems, sediments are the major recipients for these pollutants. With the addition of analyte separation capabilities (which is becoming more routine) allowing for speciation studies, PSA offers powerful analytical tools to help contract laboratories, research teams and regulators alike with these determinations.
Read MoreUSING ATOMIC FLUORESCENCE SPECTROMETRY FOR THE DETERMINATION OF MERCURY, ARSENIC, SELENIUM & ANTIMONY FROM FOOD, FEED AND BEVERAGE SAMPLES
The consumption of food and drink is one of the main sources of exposure to toxic metals. Selenium, is an essential nutritional element and is often added as a supplement
to food for health benefits. It is also an important element in animal feed to ensure livestock wellbeing. Coupling Atomic Fluorescence Spectrometry (AFS) with either cold vapour generation or hydride generation has been PSA’s core
competency for over 35 years.
ONLINE WASTEWATER ANALYSIS FOR THE DETERMINATION OF MERCURY(Hg), ARSENIC (As), SELENIUM (Se) AND ANTIMONY (Sb) USING ATOMIC FLUORESCENCE SPECTROMETRY
In recent years wastewater treatment plants have been installing technologies to capture and remove the metals. The efficiency of these treatment processes needs to be monitored using accurate analytical systems.PS Analytical offers 2 fully automated online wastewater analysers are PSA 10.226 Online Hg and PSA 10.256 Online Excalibur (for As/Se)
Read MoreWHAT IS RAMAN SPECTROSCOPY?
Raman spectroscopy is a molecular analysis technique that has been adopted by industrial, forensic, environmental and research scientists to: • Identify and quantify unknown materials (e.g., Forensic evidence, art restoration) • Understand molecular structure (e.g., crystallinity, polymorphism) • Study spatial relationships between sample components (e.g., failure/defect analysis, depth profiling) Advantages of Raman Spectroscopy You may…
Read More